Quick Start Guide
1 Introduction
This Quick Start Guide explains the basics: how to connect and set up your target on the network; how to install the SDK; and how to build the firmware images. The Linux Software Developer’s Kit (SDK) is an embedded hardware and software suite that enables Linux developers to create applications on Dusun’s DSGW-014 gateway. Base on the 4.4 Linux kernel, and leveraging existing open source software, the SDK simplifies the process of adding custom applications. Device drivers, GNU toolchain, Pre- defined configuration profiles, and sample applications are all in included.
2 Gateway Information
2.1 Basic information
SOC: RockChip PX30 Quad-core ARM Cortex-A35 Mali-G31 GPU Power Supply: POE LTE module: EG91 Wi-Fi module: 6221A (Wi-Fi chip: RTL8821CS) Lora: SX1302 eMMC: 16GB SDRAM: 2GB
2.2 Interface

3 Target Setup
This section describes how to connect the gateway into your host computer and network.
- Connecting a gateway – Power 1) Make sure that the power adapter is POE. 2) Select the appropriate power plug adaptor for your geographical location. Insert it into the slot on the Universal Power Supply; then plug the power supply into an outlet. 3) Connect the output plug of the power supply to the gateway
- Connecting a gateway – USB port 1) Connect one end of the USB cable to the USB port on the laptop or desktop 2) Connect the other end of USB cable to the USB port on the gateway.
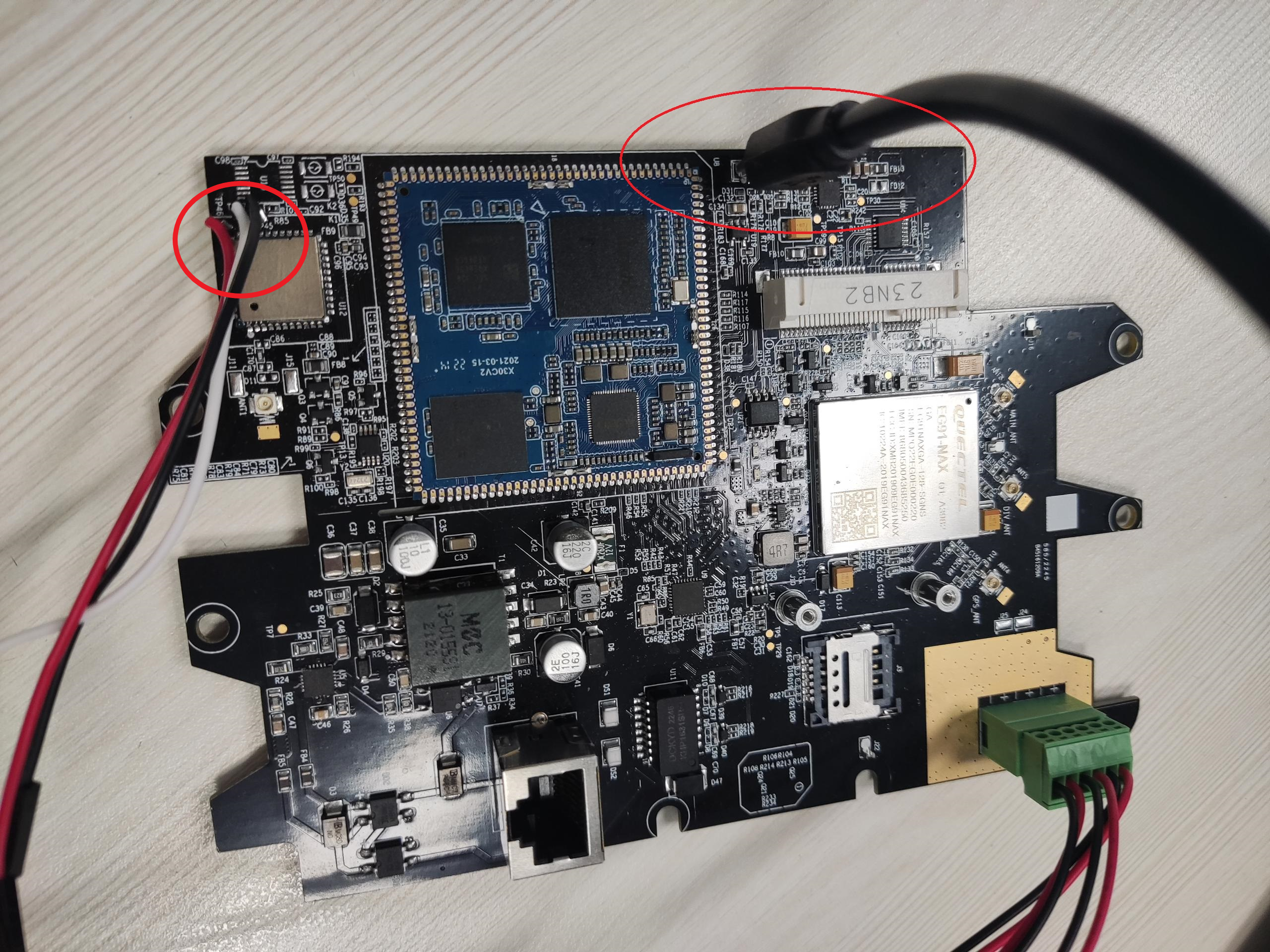
Figure3-1. Connecting a gateway via USB port
- Connecting a PCBA board – Serial Port If you want to debug the gateway, you can open the shell, Connect the PC to the PCBA board via Serial to USB tool. PIN in board for serial connection: TP45:GND TP46: RX TP47: TX
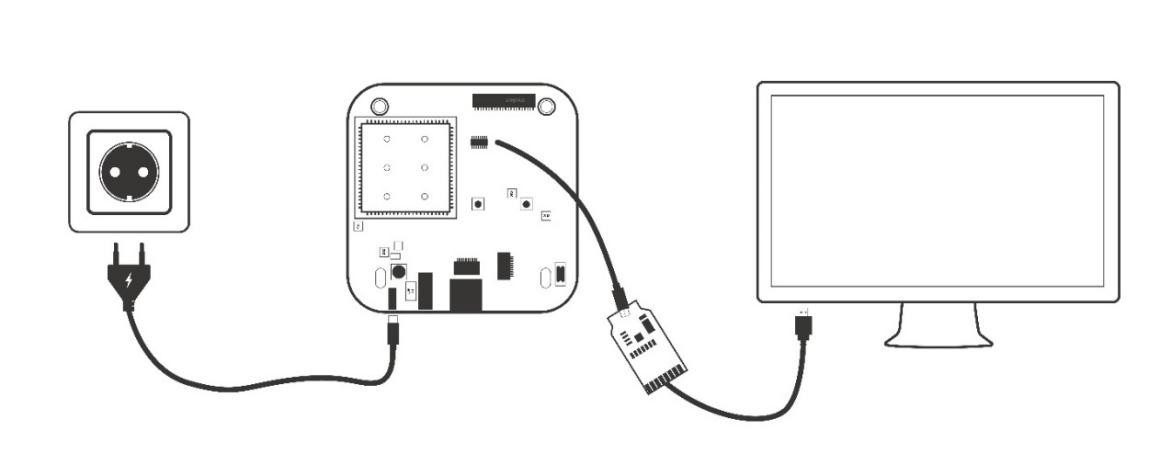
Figure3-2. Connecting a PCBA via Serial-USB tool
4 Compile the Environment to Build
Please use ubuntu 18.04 .iso image to setup your build environment. You can use a virtual machine or a physical PC to install ubuntu 18.04.
4.1 Virtual Machine
It is recommended that novice users use virtual machines, install ubuntu 18.04 to the virtual machine, and leave enough disk space (at least 100G) for the virtual machine.
4.2 Ubuntu PC Compile the Environment to Build
The use of physical machine compilation users can use a ubuntu PC.
5 SDK Acquisition and Preparation
5.1 Download the source code from the Dusun FTP
The source package name will be px30_linux-*.tar.gz, get it from Dusun FTP.
5.2 Code Compression Package Check
The next step can be taken only after generating the MD5 value of the source compression package and comparing the MD5 value of the MD5 .txt text to confirm that the MD5 value is the same, and if the MD5 value is not the same, the energy code pack is damaged, please download it again.
$ md5sum px30_linux-*.tar.gz
MD5.txt
058e13da1e4212dba0faf5666c0303b2 px30_linux.tar.gz
5.3 The Source Compression Package is Unzipped
Copy the source code to the corresponding directory and unzip the source code compression package.
$ sudo -i
$ mkdir workdir
$ cd workdir
$ tar -zxvf /path/to/px30_linux-*.tar.gz
$ cd px30_linux
6 Code Compilation
6.1 Getting started, global Compilation
6.1.1 Start Compiling
$ ./build.sh
Build a complete directory of firmware files: out/update-linux.img and other separate images, update-linux.img includes all firmware for full upgrade. The build will take a long time, please wait patiently. After update.img is built, burn it to the board according to chapter 7.
6.1.2 Prepare the Root File System base
You can build buildroot, debian rootfs image.This section is for building debian file system.
If you want to build the buildroot file system, skip this section.
- Compile Debian
Download the root file system compression package DSGW-014_debian-rootfs.zip .Unzip the compression package
$ unzip DSGW-014_debian-rootfs.zip // you get linaro-rootfs.img
Copy the root file system to the specified path
$ cd workdir/px30_linux
$ mkdir debian
$ cp ./linaro-rootfs.img ./debian/
Diff buildcofig in mk.sh
$vi mk.sh
build_buildroot()
{
cp -v ${BS_DIR_OUTPUT}/../debian/linaro-rootfs.img ${BS_DIR_OUTPUT}/rootfs.img || return 1
return 0
}
6.1.3 Run The Image on the board
Connect the PX30 board serial port to the PC via a USB to UART Bridge. Use Putty or other Terminal software as your console tool, SERIAL CONSOLE SETTINGS:
- 115200/8N1
- Baud: 115200
- Data Bits: 8
- Parity Bit: No
- Stop Bit: 1
Power UP the board, you can see the boot log on console:
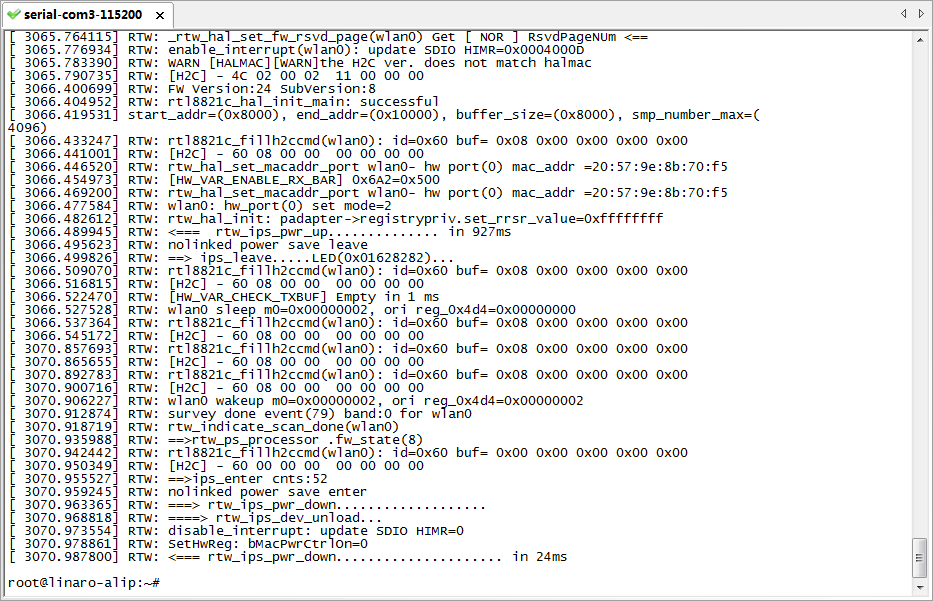
There is default password (root) for system login.
6.2 Compiled Each Image Part Separately
6.2.1 The build system and the image structure
The update-linux.img is composed of several parts. Main parts are uboot.img, boot.img, recovery.img, rootfs.img. uboot.img contains bootloader uboot boot.img contains the device tree .dtb image, Linux kernel image recovery.img: The system can boot up to recovery mode, recovery.img is the rootfs used in recovery mode. rootfs.img: The normal rootfs image. In normal mode, system boot and mount this rootfs image.
You may need to build the images separately, especially when you focus on single module (e.g. uboot or kernel driver) development. Then you can build only that part of image and update that partition in flash.
6.2.2 Build Uboot only
$ ./mk.sh -u
6.2.3 Build Linux Kernel Only
$ ./mk.sh -k
6.2.4 Build Recovery File System Only
$ ./mk.sh -r
6.2.5 Build File System Only
$ ./mk.sh -b
6.2.6 Final Image Packaging
$ ./build.sh -U
This command making output/*.img scatter firmware packaging builds in the directory update-linux.img
7 More about system and hardware
If you use configuration of system and hardware peripherals,please refer to the following
7.1 Test hardware components
The following testing are done under the system.
7.1.1 Test Wi-Fi as AP
The "ds_conf_ap.sh" script is for setting up Wi-Fi AP, SSID is "dsap", password is "12345678".
# ds_conf_ap.sh
192.168.10.1
start hostapd
Configuration file: /etc/hostapd.conf
wlan0: interface state UNINITIALIZED->COUNTRY_UPDATE start dnsmasq
Stopping dnsmasq: OK Starting dnsmasq: OK Done!!!!!!
#
#
# iwconfig
lo no wireless extensions.
wlan0 IEEE 802.11an ESSID:"dsap" Nickname:"<WIFI@REALTEK>" Mode:Master Frequency:5.745 GHz Access Point: 20:57:9E:8B:70:F5 Bit Rate:72.2 Mb/s Sensitivity:0/0
Retry:off RTS thr:off Fragment thr:off Encryption key:off
Power Management:off
Link Quality=1/100 Signal level=1/100 Noise level=0/100 Rx invalid nwid:0 Rx invalid crypt:0 Rx invalid frag:0
Tx excessive retries:0 Invalid misc:0 Missed beacon:0 eth0 no wireless extensions.
#
# ifconfig
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 0A:11:D3:88:1E:B5
inet addr:192.168.1.4 Bcast:192.168.1.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::811:d3ff:fe88:1eb5/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:73386 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:52722 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:64535523 (61.5 MiB) TX bytes:4975499 (4.7 MiB)
Interrupt:40
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0 inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host
UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:65536 Metric:1
7.1.2 Test Wi-Fi as STA
Config /etc/wpa_supplicant.conf
#cat /etc/wpa_supplicant.conf
ctrl_interface=/var/run/wpa_supplicant
ctrl_interface_group=0
update_config=1
network={
ssid=" shu fang @``` "
psk="dl123456"
disabled=1
}
network={
ssid="AAAAAA"
scan_ssid=1
psk="12345678"
key_mgmt=WPA-PSK
priority=2
}
#
#
# iwconfig wlan1
wlan1 unassociated Nickname:"<WIFI@REALTEK>"
Mode:Managed Frequency=2.412 GHz Access Point: Not-Associated
Sensitivity:0/0
Retry:off RTS thr:off Fragment thr:off
Encryption key:off
Power Management:off
Link Quality:0 Signal level:0 Noise level:0
Rx invalid nwid:0 Rx invalid crypt:0 Rx invalid frag:0
Tx excessive retries:0 Invalid misc:0 Missed beacon:0
#
#wpa_supplicant -B -d -i wlan1 -c /etc/wpa_supplicant.conf
#
#
#udhcpc -i wlan1
7.1.3 Test LTE
/usr/bin/bg96_dial.sh is used for LTE dial.
# ifconfig eth0 down
#
AT+CPIN?
+CPIN: READY
OK AT+CSQ
+CSQ: 31,99
OK
...
sent [IPCP ConfAck id=0x1]
rcvd [IPCP ConfNak id=0x3 <addr 172.28.36.150> <ms-dns1 221.131.143.69> <ms-dns2 112.4.0.55>] sent [IPCP ConfReq id=0x4 <addr 172.28.36.150> <ms-dns1 221.131.143.69> <ms-dns2 112.4.0.55>] rcvd [IPCP ConfAck id=0x4 <addr 172.28.36.150> <ms-dns1 221.131.143.69> <ms-dns2 112.4.0.55>]
Could not determine remote IP address: defaulting to 10.64.64.64 local IP address 172.28.36.150
^Z[1]+ Stopped bg96_dial.sh
#
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0 inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host
UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:65536 Metric:1
RX packets:131 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:131 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1
RX bytes:12350 (12.0 KiB) TX bytes:12350 (12.0 KiB)
ppp0 Link encap:Point-to-Point Protocol
inet addr:172.28.36.150 P-t-P:10.64.64.64 Mask:255.255.255.255
UP POINTOPOINT RUNNING NOARP MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:6 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:6 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:3
RX bytes:96 (96.0 B) TX bytes:114 (114.0 B)
wlan0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 20:57:9E:8B:70:F5
inet addr:192.168.10.1 Bcast:0.0.0.0 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::2257:9eff:fe8b:70f5/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:33387 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:56331 errors:0 dropped:636 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:5077398 (4.8 MiB) TX bytes:78164665 (74.5 MiB)
#
You need to configure APN, username/password for EG91, in quectel-chat- connect and quectel-ppp file. Before you run the test.
#cat /etc/ppp/peers/quectel-chat-connect
ABORT "BUSY"
ABORT "NO CARRIER" ABORT "NO DIALTONE" ABORT "ERROR"
ABORT "NO ANSWER" TIMEOUT 5
"" AT OK ATE0
OK AT+CPIN? READY AT
OK AT+CSQ
OK AT+QCFG="band"
OK AT+CREG?
OK ATI;+CSUB;+CSQ;+CPIN?;+COPS?;+CGREG?;&D2
#cat /etc/ppp/peers/quectel-ppp
# /etc/ppp/peers/quectel-pppd
# Usage:root>pppd call quectel-pppd
#Modem path, like /dev/ttyUSB3,/dev/ttyACM0, depend on your module, default path is /dev/ttyUSB3
/dev/ttyUSB5 115200
#Insert the Username and Password for authentication, default User and Password are test user "test" password "test" <==========================
# The chat script, customize your APN in this file
connect 'chat -s -v -f /etc/ppp/peers/quectel-chat-connect'
# The close script
disconnect 'chat -s -v -f /etc/ppp/peers/quectel-chat-disconnect'
# Hide password in debug messages hide-password
# The phone is not required to authenticate noauth
# Debug info from pppd debug
# If you want to use the HSDPA link as your gateway defaultroute
# pppd must not propose any IP address to the peer noipdefault
# No ppp compression novj
novjccomp noccp
ipcp-accept-local ipcp-accept-remote local
# For sanity, keep a lock on the serial line lock
modem dump nodetach
# Hardware flow control nocrtscts
remotename 3gppp ipparam 3gppp
ipcp-max-failure 30
# Ask the peer for up to 2 DNS server addresses usepeerdns
#
#
#Open GPS CMD:
pppcmd /dev/ttyUSB3 "AT+QGPS=1"
#Read GPS data:
cat /dev/ttyUSB1
7.1.4 Test LED
# dsled b on
# dsled g blink_fast
7.1.5 Test I2C
# i2cdetect -y 0
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f 00: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
10: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
20: -- -- -- 23 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
30: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
40: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
50: -- -- -- -- -- 55 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
60: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 6a -- -- -- -- --
70: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
#
Actually LED controlled is I2C interface.
7.2 BLE
BLE interface is /dev/ttyS1.
root@DUSUN:~# rtk_hciattach -n -s 115200 ttyS1 rtk_h5
More information about the BLE tool,use hciconfig check information.
root@DUSUN:~#hciconfig
hci0: Type: Primary Bus: UART
BD Address: B4:6D:C2:13:67:85 ACL MTU: 1021:8 SCO MTU: 255:12
UP RUNNING
RX bytes:1398 acl:0 sco:0 events:45 errors:0
TX bytes:3434 acl:0 sco:0 commands:45 errors:0
7.3 LoRaWAN
Choose the correct interface for LoRaWAN, for example /dev/spidev0.0. The configuration file for it is in /root/sx1302_hal/packet_forwarder/global_conf.json. Download "sx1302_hal_0210.tar.gz" from Dusun FTP, and copy it to board, under /root.
root@linaro-alip:~# tar xvzf sx1302_hal_0210.tar.gz
root@linaro-alip:~# cd sx1302_hal/
untar it and you can get ./sx1302_hal build LoRaWAN sample code sx1302_hal and run: More information about the LoRaWAN code, please visit https://www.semtech.com/products/wireless-rf/lora-core/sx1302 for more information.
7.4 System management configuration
The battery management chip Dusun to optimize CPU power consumption is listed,
- Adjust cpufreq parameter.
/* the default frequency scaling strategy used is interactive, relative parameters are as follows: */ ls -l /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/interactive
go_hispeed_load /* when the loading is larger than go_hispeed_load and the frequency is smaller than hispeed_freq, directly jump to hispeed_freq */
hispeed_freq /* when jumping from low frequency to high frequency, need to jump to hispedd_freq first */
above_hispeed_delay /* when the frequency is larger than hispeed_freq, the time duration before each frequency increase */
min_sample_time /* after each frequency increase, if it is to reduce the frequency next time , the time duration before frequency reduce */
target_loads /* the target loading of the frequency scaling */ timer_rate /* the loading sampling time,unit:us */
timer_slack /* the loading sampling time after cpu entering idle */
boost /* when the frequency is smaller than hispeed_freq, keep boost to hispeed_freq */
boostpulse /* when the frequency is smaller than hispeed_freq, boost to hispeed_freq, keep a while */
boostpulse_duration /* time duration of boostpulse, unit:us */ io_is_busy /* whether to compute io wait to cpu loading */
We mainly adjust three parameters: hispeed_freq,target_loads,timer_rate:
6 hispeed_freq: select an appropriate transition frequency, to make cpu stable
in the medium frequency, with the best power consumption, too large or too small will cause cpu jump to high frequency easily and increase the power consumption.
7 target_loads:easier to run with low frequency after this value is increased, both the power consumption and the performance will be reduced.
8 timer_rate: easier to run with low frequency after this value is increased, both the power consumption and the performance will be reduced.
Close some cpu, limit the highest frequency of cpu
/* close cpu2,cpu3 */
echo 0 > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu2/online echo 0 > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu3/online
/* List all the available frequency */
cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/scaling_available_frequencies output: 408000 600000 816000 1008000 1200000 1296000
/* set the max frequency of cpu0 to 1200MHz */
echo 1200000 > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/scaling_max_freqSoC with ARM Big-Little architecture can bind the tasks with high loading to little cores through CPUSET since the energy efficiency of the little core is better. / Note: SoC with SMP architecture can also bind the tasks to some cpu so that other cpus can enter low power consumption mode, but maybe it will make cpu easy to run with high frequency, which will increase the power consumption. /*
/* create group of litte core*/ mkdir /dev/cpuset/little
/* set cpu used by group of little core */ echo 0-3 > /dev/cpuset/little/cpus
/* add pid=1111 task into the group of little core */ echo 1111 > /dev/cpuset/little/tasks
/* Android system creates several groups by default, the framework layer puts the tasks into differenct groups, you can adjust cpus of each group, analyze the power consumption */
ls /dev/cpuset background foreground
system-background top-app
- Limit the cpu bandwidth of the tasks with high loading through CPUCTL (need to enable the macro CONFIG_CFS_BANDWIDTH).
/* create the group of bandwidth limitation */ mkdir /dev/cpuctl/mygroup
/* set the cycle of bandwidth limitation as 10ms */ echo 10000 > /dev/cpuctl/mygroup/cpu.cfs_quota_us
/* within each cycle, total running time of the tasks in the group cannot exceed 5ms, this value can be larger than cfs_quota_us, because it is the total running time of multiple cpus */
echo 5000 > /dev/cpuctl/mygroup/cpu.cfs_period_us
/* add relative tasks into the group */ echo 1111 > /dev/cpuctl/mygroup/tasks echo 1112 > /dev/cpuctl/mygroup/tasks
/* cpu.shares means to limit the bandwidth of the task through weight, used for performance optimization, without affecting the power consumption */
/dev/cpuctl/mygroup/cpu.shares
8 Image Upgrade
8.1 Upgrade Tool
Upgrade tool:AndroidTool_Release_v2.69
Upgrade driver:DriverAssitant_v4.91
use the upgrade tool, must first exe DriverInstall.exe in DriverAssitant_v4.91
8.2 Go into Upgrade Mode by ADB Switch
- Connect the OTG port to the burning computer USB port, it's also act as POE power supply
- click ADB switch in AndroidTool
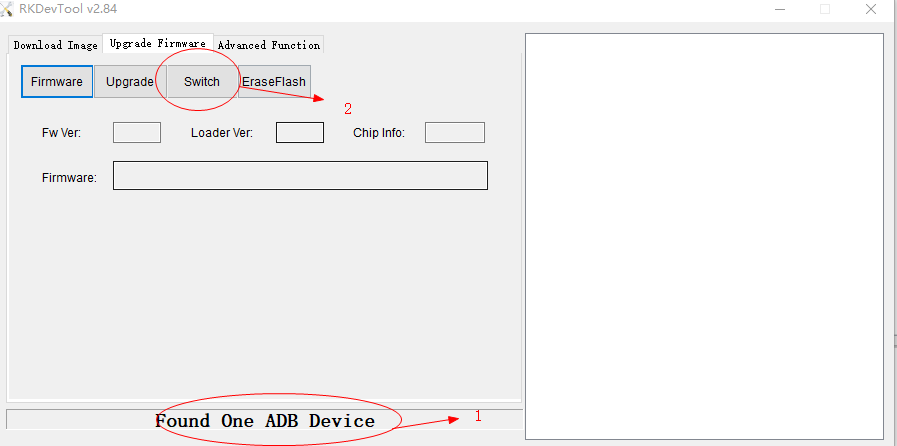
8.3 Go into Upgrade Mode by Serial
Connect the OTG port to the burning computer USB port, it's also act as POE power supply
Press "Ctrl+C" when uboot is booting up, to enter uboot:
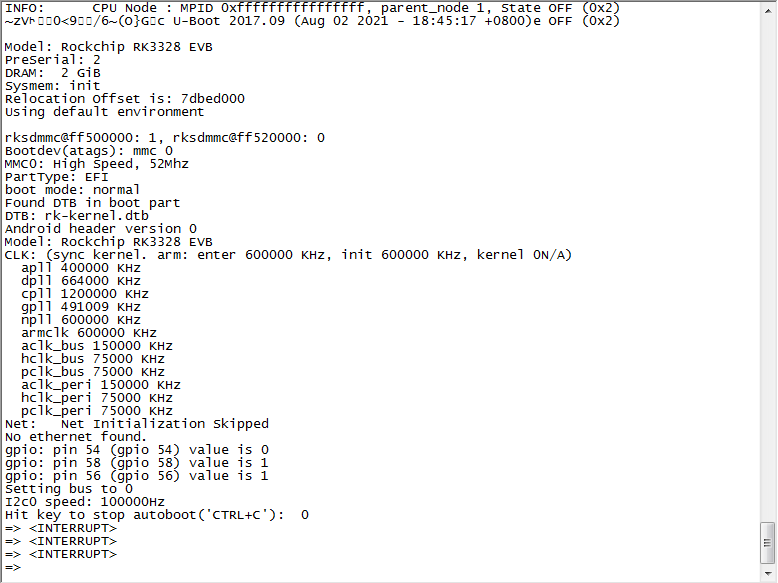
3.uboot "rbrom" comand to reboot the board into maskrom mode, for a complete "update.img" upgrade.
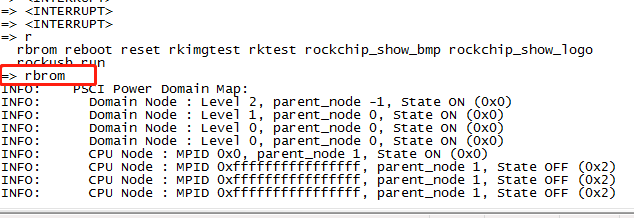
4."rockusb 0 mmc 0" command to reboot board to loader mode, for a partial firmware upgrade or a complete "update.img" upgrade.
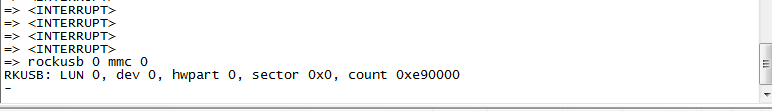
8.4 The Entire Package of Firmware "update-linux.img" Upgrade
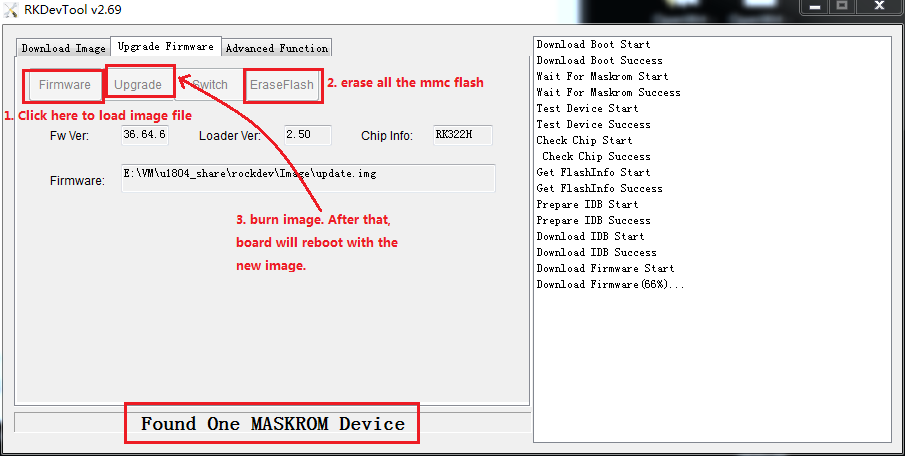
8.5 Upgrade the Firmware Separately
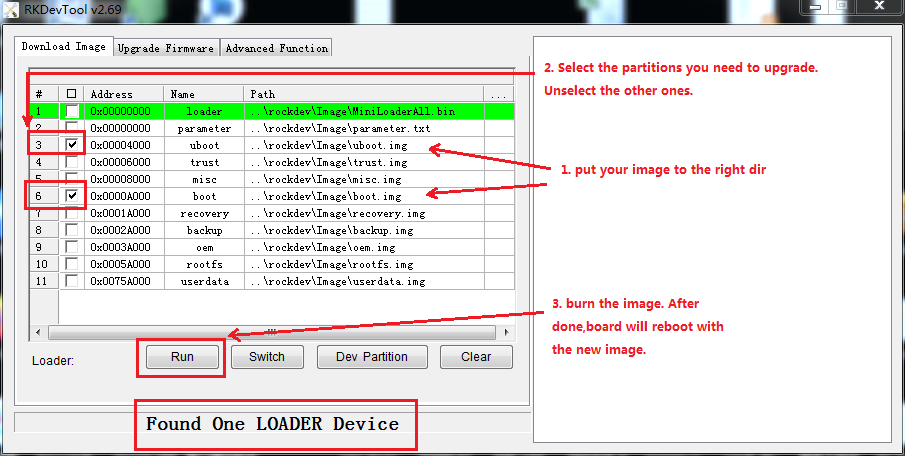
9 Read firmware image from gateway
Steps for read firmware image from the gateway by Serial is shared below.
Restart to recovery mode bootm2recovery.sh
killall dsupdateimg
mount /dev/mmcblk1p9 /f
dd if=/dev/mmcblk1p8 of=/f/rootfs.img bs=10M
Restart to normal Debian mode again, copy /f/rootfs.img to the server and save.
Then You have the file system you need.