Quick Start Guide
1 Introduction
1.1 Purpose & Description
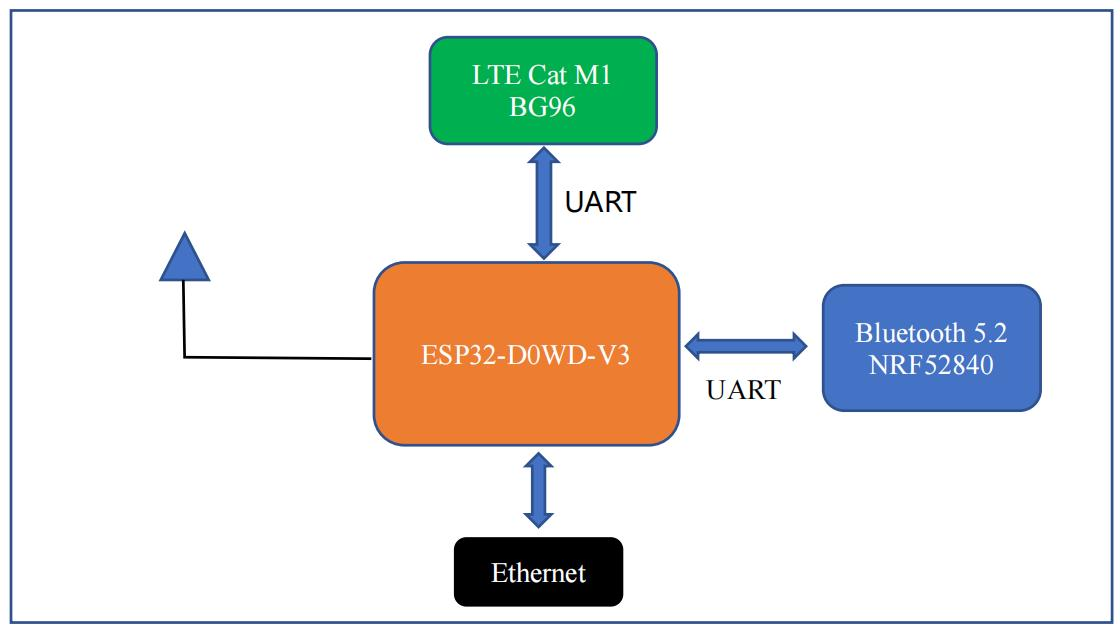
The Bluetooth gateway solution based on ESP32 and Nordic nRF52840 chips is a cost-effective and reliable solution for connecting Bluetooth-enabled devices to the cloud. The ESP32 chip is a low-power, high-performance microcontroller with integrated Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. It supports multiple low-power operating modes and has a rich peripheral interface. The Nordic nRF52840 chip is a multi-protocol Bluetooth 5.2 and 802.15.4 wireless system-on-chip with a high performance and ultra-low power consumption. It supports a wide range of Bluetooth Low Energy applications and is compatible with multiple wireless protocols.
The combination of ESP32 and nRF52840 chips provides a comprehensive solution for Bluetooth gateway applications. The ESP32 chip is responsible for collecting data from Bluetooth-enabled devices and transmitting it to the cloud. The nRF52840 chip is responsible for establishing a secure connection between the ESP32 and the cloud. The two chips work together to provide a secure and reliable connection between the device and the cloud.
The solution is ideal for a variety of applications, such as home automation, health monitoring, and industrial automation. It offers a cost-effective, secure, and reliable solution for connecting Bluetooth-enabled devices to the cloud.
1.2 SDK
Espressif SDK can be obtained from the following URL: https://github.com/espressif/esp-idf.git. This SDK contains the necessary components for developing applications for Espressif's range of ESP32 and ESP8266 microcontrollers.
Nordic SDK can be obtained from the following URL: https://developer.nordicsemi.com/nRF5_SDK/nRF5_SDK_v17.x.x/nRF5_SDK_17.1.0_ddde560.zip. This SDK contains the necessary components for developing applications for Nordic's range of nRF51 and nRF52 microcontrollers.
1.3 Hardware block diagram
2 Examples
2.1 WiFi iperf example (for esp32)
The iperf example doesn't support all features in standard iperf. It's compitable with iperf version 2.x. You can find the source code and the project file of the example in the following folder: esp-idf/examples/wifi/iperf
This example implements the protocol used by the common performance measurement tool iPerf.
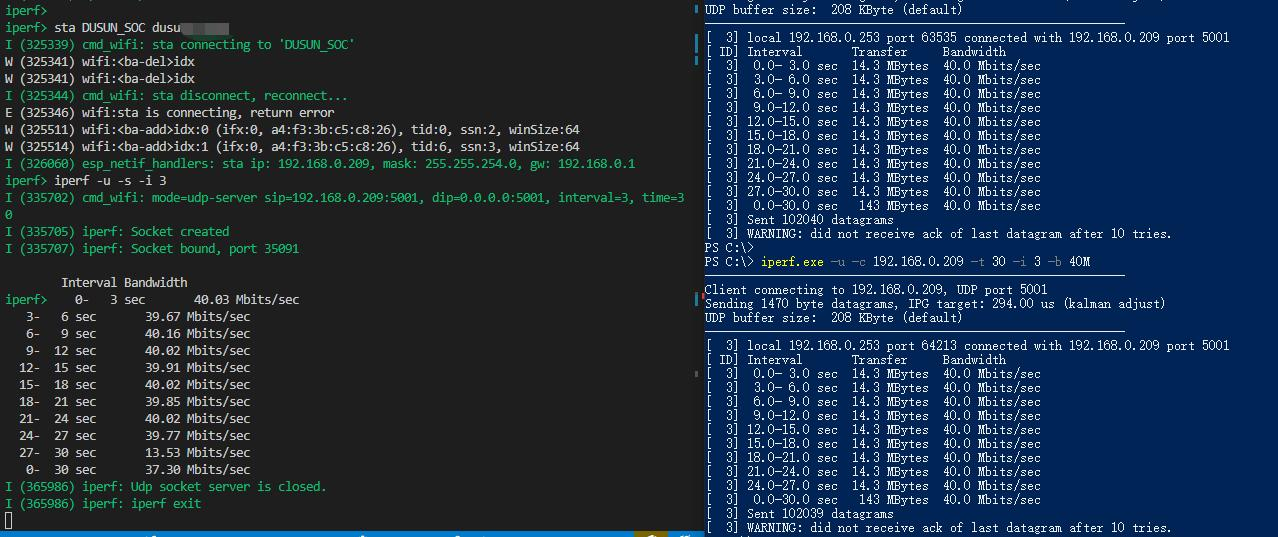
Performance can be measured between two ESP32s running this example, or between a single ESP32 and a computer running the iPerf tool Demo steps to test station TCP Rx performance:
- Build the iperf example with sdkconfig.defaults, which contains performance test specific configurations
- Run the demo as station mode and join the target AP
sta ssid password
- Run iperf as server on ESP32 side
iperf -u -s -i 3
- Run iperf as client on PC side
iperf -u -c 192.168.0.209 -i 3 -t 30 -b 40M
The console output, which is printed by station UDP RX throughput test, looks like:
2.2 Ethernet iperf example (for esp32)
The iperf example doesn't support all features in standard iperf. It's compitable with iperf version 2.x. You can find the source code and the project file of the example in the following folder: esp-idf/examples/ethernet/iperf
YT8512H driver modification method: YT8512H is compatible with RTL8201. It only needs to modify the Chip ID and PHY ADDR.
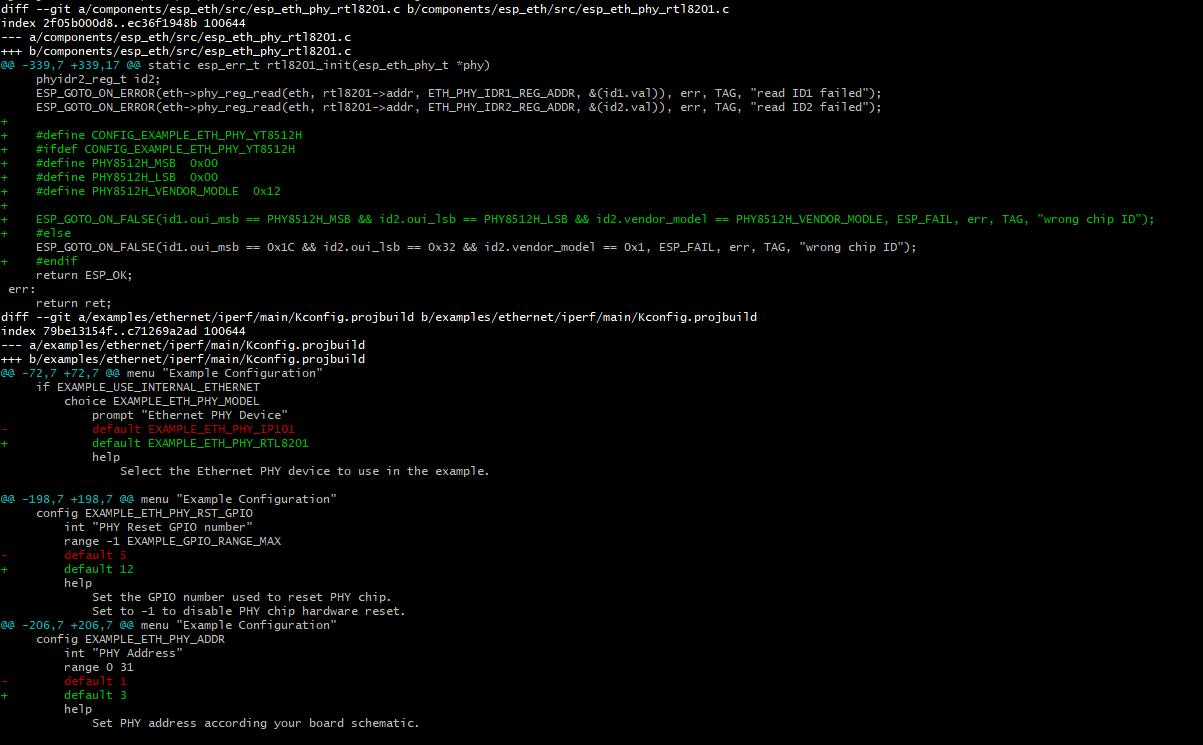
This example implements the protocol used by the common performance measurement tool iPerf. Performance can be measured between two ESP32s running this example, or between a single ESP32 and a computer running the iPerf tool Demo steps to test station TCP Tx performance:
- Build the iperf example with sdkconfig.defaults, which contains performance test specific configurations
- Run iperf as server on PC side
iperf -u -s -i 3
- Run iperf as client on ESP32 side
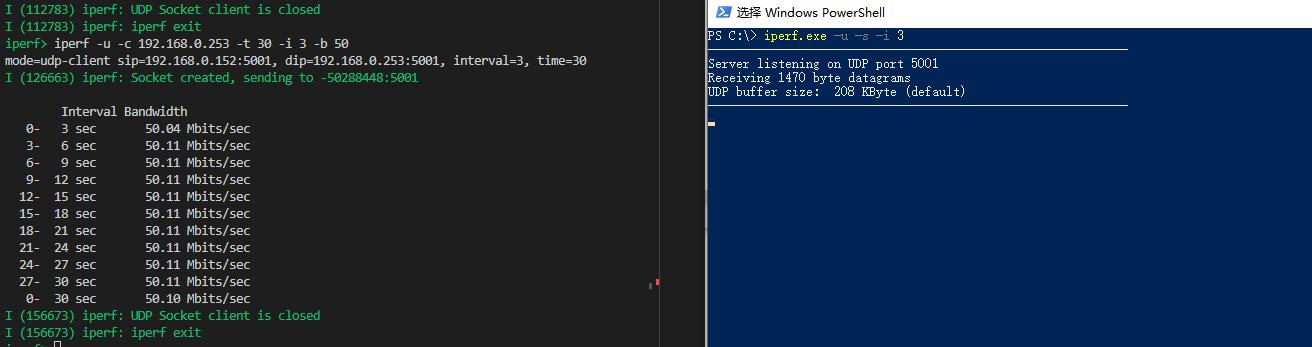
iperf -u -c 192.168.0.253 -i 3 -t 30 -b 50
The console output, which is printed by station UDP TX throughput test, looks like:
2.3 BLE Interactive Command Line Interface Example (for nrf52840)
The BLE Interactive Command Line Interface Example demonstrates how to control a BLE application using a command line interface. A set of generic BLE commands is provided. The application can be connected to several peripheral and central devices and interact with them. Dynamic subcommands are used to select a peer to interact with based on its BLE device address.
Main application features: Scanning and advertising.
- Private advertising. Multiple central and peripheral connections.
- Connecting with a private peer.
- Connection parameter negotiation.
- Other Link Layer parameter negotiation: Data Length and PHY.
- ATT MTU length negotiation.
- Requesting security (pairing, bonding).
- OOB pairing using NFC as a BLE central or peripheral device.
- GATT Client commands.
- Device Name change
The BLE Interactive Command Line Interface Example can be used with multiple nRF52840 as well as any other BLE devices. Use console BLE commands to interact with other BLE devices. Additionally, the application includes the Battery Service to demonstrate GATT Server behavior.
This example demonstrates the use of Low Energy Secure Connections (LESC). The default cryptographic backend used for LESC is CC310 (when run on nRF52840) or Oberon (for other SoCs). To use micro-ecc instead, follow the steps in Enabling micro-ecc support in selected examples. You can find the source code and the project file of the example in the following folder: nRF5_SDK_17.1.0_ddde560\examples\ble_central_and_peripheral\experimental\ble_app_interactive\pca10056\s140
- BLE Commands
The application BLE commands are organized in a tree structure
- Root Commands
advertise - Turn advertising on or off.
bonded_devices - List bonded_devices
connect - <address/peer_id> Establish a connection with a device.
connected_devices - Display connected devices and security information on eachconnection.
device_name - <name> Set device name.
devices - List available (advertising) devices.
disconnect - <address> Disconnect from a device.
gatt - GATT Client procedures.
key_reply - <key> Enter passkey displayed by another device (for pairingmode: "Passkey Entry").
nfc_read - <subcmd> Turn on NFC reader (requires additional hardware)<on/off>.
numeric - Confirm or reject a numerical value (for pairing mode:"Numerical Comparison").
pair - <subcmd> <address> <option> Initiate pairing with a connecteddevice.
parameters - <subcmd> Change or request new Link Layer or GATT parameters.
privacy - Set privacy settings.
remove_bond - <subcmd> Remove a bonded device.
scan - Turn scanning on or off.
- Subcommands tree
├── advertise
│ ├── on Start advertising and activate the on-chip NFC Tag.
│ └── off Stop advertising and deactivate the on-chip NFC Tag.
|
├── bonded_devices
│ ├── connect <address/peer_id>
│ ├── connected_devices
│ ├── devices List advertising devices.
│ ├── disconnect <address>
│ ├── Catt
| | ├── characteristics <address> <service quid> Discover service characteristics.
│ | │
│ | ├── indication Change indications state.
│ │ ├── on <address> <characteristic quid> On indications.
│ │ └── off <address> <characteristic quid> Off indications.
│ │
│ ├── notification> Change notifications state.
│ │ ├── on <address> <characteristic quid> On notification.
│ │ └── off <address> <characteristic quid> Off notification.
│ │
│ ├── read <address> <characteristic quid> Read a characteristic value.
│ │
│ ├── services <address> Discover services.
│ └── write <sub_cad> Write a characteristic value.
│ ├── command <address> <char quid> <value> Use a Write Command.
│ └── request <address> <char quid> <value> Use a Write Request.
├── key_reply <key> Type a passkey (in pairing mode: "Passkey Entry").
│
├── NFC_read
│ ├── on Turn on NFC tag reading (requires additional hardware), if an NDEF Messagefor BLE pairing is read, connecting and pairing are performed automatically.
│ └── off Turn off NFC tag reading.
│
├── numeric
│ ├── accept a numerical value (in pairing mode: "Numerical Comparison")
│ └── reject a numerical value (in pairing mode: "Numerical Comparison").
│
├── pair
│ ├── LEGACY <address> <option> Start pairing (use BLE Legacy pairing).
| └── LESC <address> <option> Start pairing (use BLE Secure Connections pairing).
│
├── parameters
│ ├── apply <address> Apply the currently set connection parameters (start negotiation,or change parameters - depending on the BLE role).
│ ├── data_length <address> <value> Request Data Length change.
│ ├── max_Conn_interval <value> Set maximum connection interval.
│ ├── min_Conn_interval <value> Set minimum connection interval.
│ ├── Btu <value> Request Ab MTU length change.
│ ├── pay <subsumed> <address> PHY change.
│ ├── slave_latency <value> Set slave latency.
│ └── sup_timeout <value> Set connection supervision timeout.
│ ├── privacy Set privacy settings for advertising.
│ ├── on Turn on privacy.
│ └── off Turn off privacy.
|
├── remove_bond
│ ├── all Remove all bonded devices.
│ └── device <address> Remove a selected bonded device.
│
└── scan
├── on Start scanning.
└── off Stop scanning.
Test the BLE Interactive Command Line Interface Example application, for example by performing thefollowing steps:
- If you are using the software backend of the Cryptography library - nrf_crypto, ensure that you have
installed and enabled the micro-ecc library.
- Compile and program the application on test board.
- Start a terminal emulator such as PuTTY(recommended) using the following terminal Settings as well asUART and USB Settings or RTT Settings. Or connect to the UART of nrf52840 through the UART of
ESP32.
- Open a serial connection to the COM port used by the tester board. A command prompt is displayed.
- Type scan on in the terminal to start scanning BLE devices.
- Type devices to display list of available (advertising) devices. The list is periodically refreshed in the
background.
Type connect to connect to a device. You can use the device addresses displayed earlier. The
addresses will display as dynamic subcommands (press 'Tab' for auto-fill).
After establishing the connection, you can use other commands defined in the application. For example:
Type pair to initiate pairing with a device.
Type parameters to set new connection parameters or negotiate ATT MTU, PHY, or Data Length.
Type gatt to use GATT Client commands.
- You can also start scanning again and connect to another device, or start advertising to become connectable
for other devices.
- The application supports multiple connections in both roles (central and peripheral). The commands can be
directed to any connected device using its BLE device address.
- Type disconnect to disconnect from a device.
- These steps can be repeated using two boards with the same application. Then, both boards work in differentconfigurations, for example as a scanner or an advertiser, a central or a peripheral device etc.
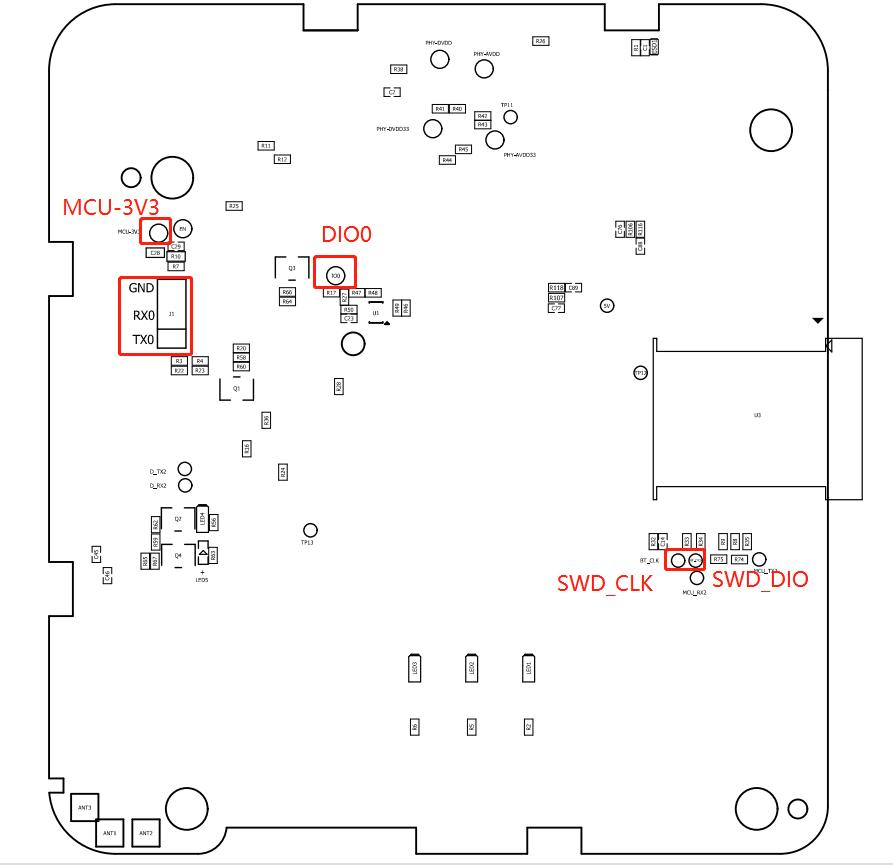
3.Download interface description
The interface for downloading ESP32 chip is UART, and the interface for downloading nRF52840 is SWD.